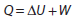Understandings:
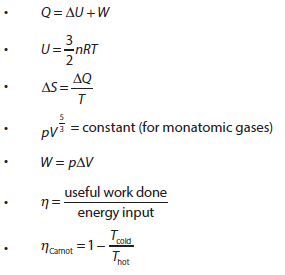
- The first law of thermodynamics
- The second law of thermodynamics
- Entropy
- Cyclic processes and pV diagrams
- Isovolumetric, isobaric, isothermal and adiabatic processes
- Carnot cycle
- Thermal efficiency
Applications and skills:
- Describing the first law of thermodynamics as a statement of conservation of energy
- Explaining sign convention used when stating the first law of thermodynamics as
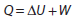
- Solving problems involving the first law of thermodynamics
- Describing the second law of thermodynamics in Clausius form, Kelvin form and as a consequence of entropy
- Describing examples of processes in terms of entropy change
- Solving problems involving entropy changes
- Sketching and interpreting cyclic processes
- Solving problems for adiabatic processes for monatomic gases using 5 pV 3 = constant
- Solving problems involving thermal efficiency
- Solving problems involving the first law of thermodynamics
- Describing the second law of thermodynamics in Clausius form, Kelvin form and as a consequence of entropy
|
International-mindedness:
- The development of this topic was the subject of intense debate between scientists of many countries in the 19th century
Utilization:
- This work leads directly to the concept of the heat engines that play such a large role in modern society
- The possibility of the heat death of the universe is based on ever-increasing entropy
- Chemistry of entropy (see Chemistry sub-topic 15.2)
Aims:
- Aim 5: development of the second law demonstrates the collaboration involved in scientific pursuits
- Aim 10: the relationships and similarities between scientific disciplines are particularly apparent here
|